FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions
Here you will find answers to the most common questions about our products, services, and offerings. Should your concern not be addressed, our support team is available to assist you personally at any time.
Questions about our Products
Saw Blade Construction
What Types of Saw Blade Qualities are Available?
WESPA offers tool steel, bimetal, carbide, and diamond-grit bands.
Why are there Different Types of Saw Blades?
Every material and every application has its own requirements. That is why there are specially adapted types.
What is a Carbide Saw Blade?
A band with ground carbide tooth tips that allows for higher cutting speeds.
What is a Bimetal Saw Blade?
A band made of two metals: flexible tempered steel as the backing and hardened HSS for the teeth.
Why are the Backing Strip and Tooth Tips Made of Different Materials?
The backing strip is flexible and robust, while the tooth tips are extremely hard. This combines stability with wear resistance.
What are the Advantages of a Variable Tooth Pitch?
It reduces vibrations during sawing and allows for more flexible applications across various workpiece dimensions.
What Does "TPI" Mean?
“TPI” stands for Teeth Per Inch. This refers to the number of teeth per 25.4 mm of blade length.
What is the Difference between Constant and Variable Tooth Pitch?
Constant: all tooth pitches are equal.
Variable: the pitches vary within an interval.
IPC Saw Blade Upgrade
What Does IPC Mean at WESPA?
IPC stands for Individual Performance Cutting – a concept developed by WESPA for the individual configuration of saw blades, tailored to the specific application and customer requirements.
What IPC Options are Available and What Do They Achieve?
IPC C (Coating-C): Coating for saw blades for increased tool life and cutting performance.
IPC S (S-Wave): Mechanical back edge modification for hard materials.
IPC X (X-Set): Special tooth set for reduced tooth breakage.
IPC H (Honing): Pre-rounding of the tooth tips to eliminate the need for saw blade run-in.
How is the Appropriate IPC Configuration Determined?
Through a technical analysis of customer requirements and operating conditions –
e.g., material, machine, cutting parameters – the optimal combination is selected.
What Advantages Does WESPA IPC Offer Compared to Standard Saw Blades?
Longer tool life, better surface quality, lower noise levels, shorter cutting times, and reduced tool costs.
Is IPC also Suitable for Older Band Sawing Machines?
Yes – IPC saw blades are particularly advantageous on machines that are not suitable for carbide.
How Does IPC Affect Productivity?
With its IPC program, WESPA enables higher feed rates, shorter cutting times, and more efficient utilization of machine capacity – without additional investments.
Which Materials Can be Processed Better with IPC?
From structural steel and stainless steel to nickel alloys and titanium – WESPA IPC options are configurable depending on the material.
How Quickly Can IPC Saw Blades be Delivered?
Thanks to optimized manufacturing processes and targeted configurations, IPC blades are available at short notice despite individualization.
What Economic Advantages Does IPC Offer?
Reduced machining costs, longer tool life, less machine downtime, and increased competitiveness.
Icons
Product Features

Standard Tooth
neutral rake angle

Claw Tooth
positive rake angle

Reinforced Claw Tooth
positive rake angle

Special Tooth
positive rake angle

Reinforced Profile Tooth
positive rake angle

Carbide Tipped
positive rake angle

Carbide Tipped
neutral rake angle

Carbide Tipped
negative rake angle
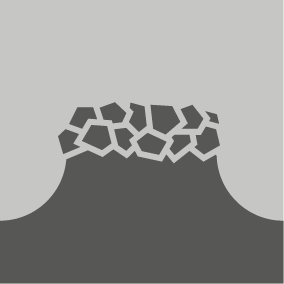
Carbide Grit
multiple rake angles

V+N Geometry
ground
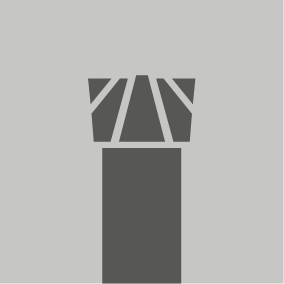
Multi-chip Geometry
ground
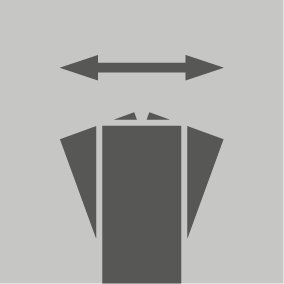
Set
extra wide
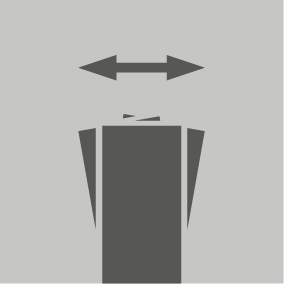
Set
wide
Applications

Solid Material
large

Solid Material
small

Tubes and Profiles
thick-walled

Tubes and Profiles
thin-walled

Steel Beams

Bundle Cutting
Solid Material

Bundle Cutting
Tubes and Profiles
Mineral Materials

Wire and Fiber-Reinforced Tires

Metal Cables and Wires

Composite Materials

Case Hardened
Product Benefits

Versatile

Precision

Surface Accuracy

Wear Resistance

Performance

Cost Reduction
Vibration and Noise Reduction
Material Classes
Material Class
1
- Non-ferrous Metals
- Aluminum
- Structural Steel
- Cast Iron
- Tempered Steel
- Case-hardening Steel
- Ball Bearings
- Tool Steel
- High-Speed Steel
Material Class
2
- Corrosion- and Acid-Resistant Steels
- Hardened Steels
- Heat-Resistant Steels
- Steel and Non-Ferrous Alloys
- Titanium - Titanium Alloys

